package com.pure.blog.test;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.DeleteMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
//사용자가 요청 -> 응답 (HTML 파일)
//@Controller
// 사용자가 요청 - > 응답 (Data)
@RestController
public class HttpControllerTest {
//브라우저에서 요청할 수 있는 것은 get 메서드 밖에 없다.
/*
* @GetMapping("/http/get") public String getTest(@RequestParam int
* id, @RequestParam String username) { return "get 요청: "+id+", "+username; }
*/
//이렇게 Member 객체로 한번에 받을 수도 있다.
@GetMapping("/http/get")
public String getTest(Member m) { //get?id=1&username=pure&password=pure1234&email=pure@gmail.com 쿼리스트링 뒤의 변수도 알아서 스프링이 매핑해줌.
return "get 요청: "+m.getId()+", "+m.getUsername()+", "+m.getPassword()+", "+m.getEmail();
}
//Post는 쿼리스트링이 아니고 Http Body에 담아서 보낸다.
//우리가 항상 써왔던 <form>태그 안의 <input>태그로 데이터를 넘긴 방식이 x-www-form-urlencoded 형식이다.
/*
* @PostMapping("/http/post") public String postTest(Member m) { return
* "post 요청: "+m.getId()+", "+m.getUsername()+", "+m.getPassword()+", "+m.
* getEmail(); }
*/
/*
* @PostMapping("/http/post") //text/plain 방식이 기본. public String
* postTest(@RequestBody String text) { return "post 요청: "+ text; }
*/
@PostMapping("/http/post") //application/json 방식으로 요청
public String postTest(@RequestBody Member m) { //MessageConverter가 파싱함.
return "post 요청: "+m.getId()+", "+m.getUsername()+", "+m.getPassword()+", "+m.getEmail();
}
@PutMapping("/http/put")
public String putTest(@RequestBody Member m) {
return "put 요청"+m.getId()+", "+m.getUsername()+", "+m.getPassword()+", "+m.getEmail();
}
@DeleteMapping("/http/delete")
public String deleteTest() {
return "delete 요청";
}
}
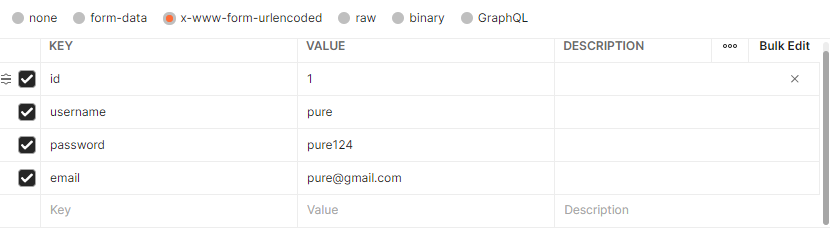
Post 방식에서 x-www-form-urlencoded 방식 이용했을 때.
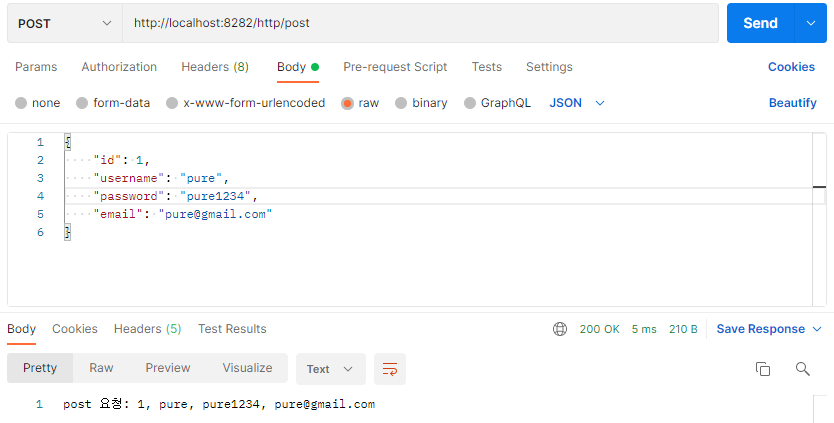
POST 방식에서 application/json 형태로 받았을 때.
JSON 형태로 보내면 MessageConverter가 알아서 파싱해줌.
핵심.
@RequestBody를 사용하면 JSON형태로 요청된 데이터가 자동으로 파싱되어 JAVA 객체로 받을 수 있다.
'취업 준비 > Spring boot' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 7. yml 설정 (0) | 2022.01.21 |
|---|---|
| 6. lombok의 builder (0) | 2022.01.21 |
| 4. HTTP1.1 체험하기 (0) | 2022.01.21 |
| 3. MySQL 설정하기 (0) | 2022.01.20 |
| 2. 의존성 설정 (0) | 2022.01.20 |
